Querying the Raphtory Server
This page demonstrates how to interact with the Raphtory Server using Python. All examples use the RaphtoryClient to send queries and mutations.
The GraphQL API mirrors the Python API - the same operations available in Python are accessible via GraphQL. For the full GraphQL schema reference, see the GraphQL API documentation.
Graphical Playground
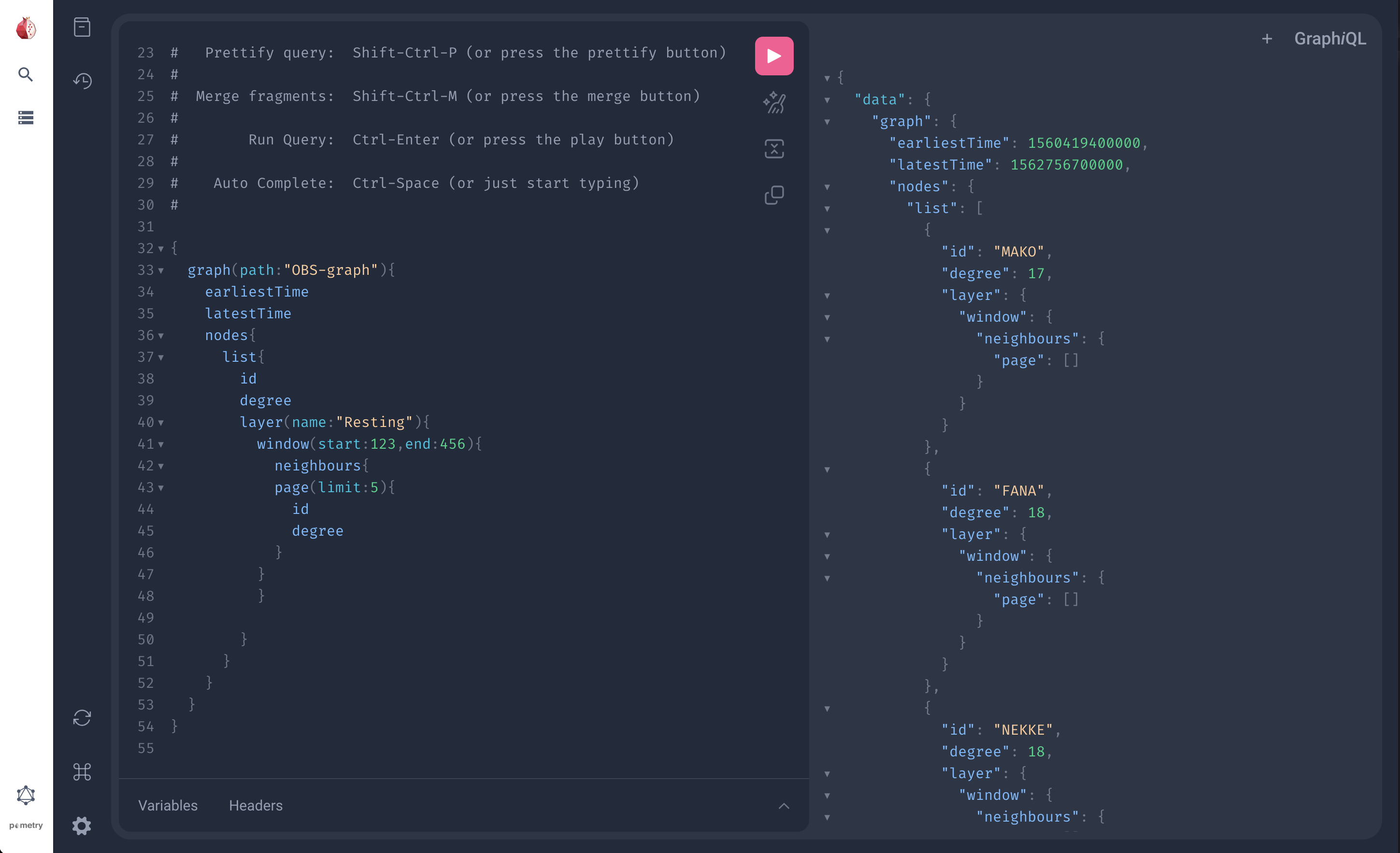
When you start a GraphQL server, you can find the GraphQL UI at localhost:1736/playground (or your specified port).
An annotated schema is available from the documentation tab in the left-hand menu.
Setup
First, let's create a sample graph and start the server:
Querying Nodes and Edges
List All Nodes
List All Edges
Node Properties
Get properties for a specific node:
Edge Properties
Get properties for a specific edge:
Graph Metadata
Query graph-level metadata:
Modifying Graphs via GraphQL
You can modify graphs using raw GraphQL queries and mutations. This gives you full control over the GraphQL API.
Creating a Graph (Mutation)
Use the newGraph mutation to create a new empty graph:
Adding Nodes
Use updateGraph to add nodes (note: this is a query, not a mutation):
Adding Edges
Copy, Move, and Delete Graphs
Python Helper Functions
For convenience, RaphtoryClient provides helper functions that wrap the GraphQL operations.
Creating a New Graph
The second parameter specifies the graph type: EVENT or PERSISTENT. See Graph Types for details.
Updating a Graph Remotely
Use remote_graph() to get a handle for adding data without downloading the full graph:
Receiving a Graph
Download a graph from the server to a local Python object:
Sending a Graph
Upload a locally-created graph to the server: